mathinschool.com
numbers and algebraic expressions
logic, sets, intervals
absolute value
function and its properties
linear function
quadratic function
polynomials
rational function
exponential function
logarithm
number sequences
limits of sequences and functions
derivative and integral of functions
trigonometry
plane geometry
analytic geometry
solid geometry
combinatorics
probability
elements of statistics
kropki game
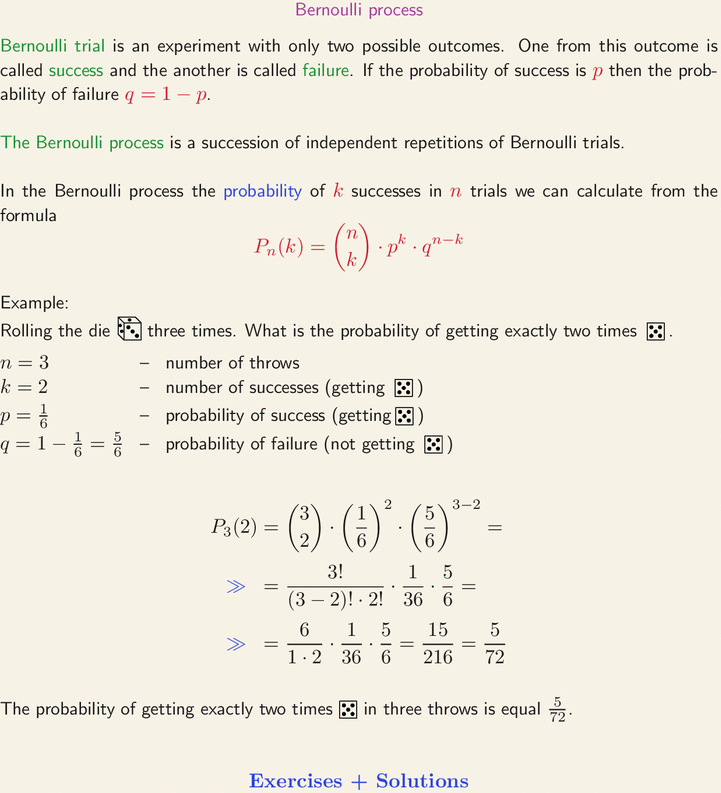
Bernoulli trial is an experiment with only two possible outcomes. One from this outcome is called success and the another is called failure. If the probability of success is p then the probability of failure q = 1 - p. The Bernoulli process is a succession of independent repetitions of Bernoulli trials. In the Bernoulli process the probability of k successes in n trials we can calculate from the formula P_n(k) = (n over k) * p^k * q^(n-k). Example: Rolling the die three times. What is the probability of getting exactly two times 5. n = 3number of throws, k = 2 number of successes (getting 5). p = 1/6 probability of success (getting 5). q = 1- 1/6 = 5/6 - probability of failure (not getting 5). P_3(2) = (3 over 2) * (1/6)^2 * (5/6)^(3-2) = 5/72. The probability of getting exactly two times 5 in three throws is equal 5/72.