mathinschool.com
numbers and algebraic expressions
logic, sets, intervals
absolute value
function and its properties
linear function
quadratic function
polynomials
rational function
exponential function
logarithm
number sequences
limits of sequences and functions
derivative and integral of functions
trigonometry
plane geometry
analytic geometry
solid geometry
combinatorics
probability
elements of statistics
kropki game
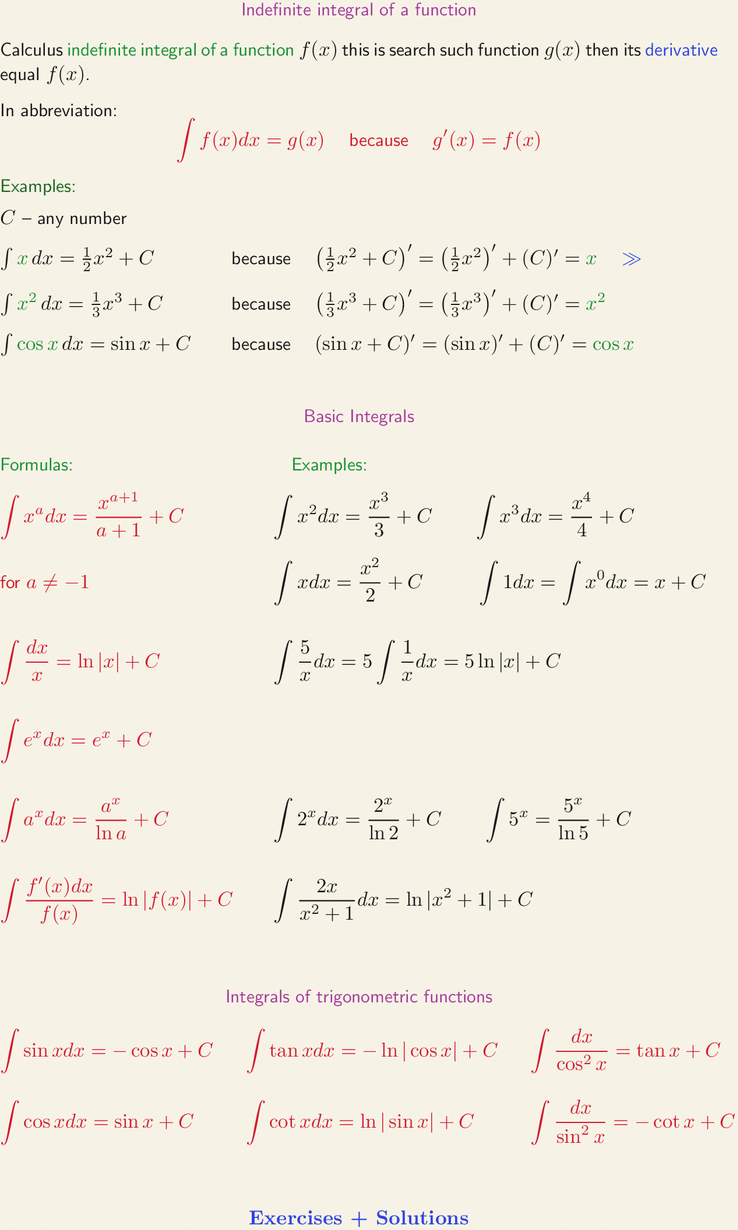
Calculus indefinite integral of a function f(x) this is search such function g(x) then its derivative equal f(x). In abbreviation: ∫ f(x) dx = g(x) because g'(x) = f(x). Examples: C - any number. ∫ x dx = 1/2 x^2 + C because ((1/2)x^2 + C)' = ((1/2)x^2)' + (C)' = x. ∫ x^2 dx = (1/3)x^3 + C because ((1/3)x^3 + C)' = ((1/3)x^3)' + (C)' = x^2. ∫(cos x)dx = sin x + C because (sin x + C)' = (sin x)' + (C)' = cos x. Basic Integrals. Formulas. Examples. ∫ x^a dx = x^{a+1} / a+1 + C. ∫ x^2 dx = x^3/3 + C, ∫ x^3 dx = x^4/4 + C. for a ≠ -1. ∫ x dx = x^2/ 2 + C, ∫ 1 dx = ∫ x^0 dx = x + C. ∫ dx / x = ln|x| + C. ∫ 5 / x dx = 5, ∫ 1 / x dx = 5 * ln|x| + C. ∫ e^x dx = e^x+C, ∫ a^x dx = a^x / ln a + C, ∫ 2^x dx = 2^x / ln2 + C, ∫ 5^x = 5^x / ln5 +C. ∫ f'(x) dx / f(x)} = ln |f(x)| + C, ∫ 2x / (x^2 + 1) dx = ln|x^2 + 1| + C. Integrals of trigonometric functions. ∫ sin x dx = -cos x + C, ∫ tan x dx = -ln|cos x| + C, ∫ dx / cos^2 x = tan x + C. ∫ cos x dx = sin x + C. ∫ cot x dx = ln |sin x| + C, ∫ dx / sin^2 x = -cot x + C.